Gum retreat occurs as gum tissue moves down along the tooth, exposing the root surface, resulting in the tooth becoming visually longer. A normally healthy gum must be twisted along the edge of the tooth crown, following its shape and filling the space between the teeth to their contact point in addition to the gums. If the gums recede, the root surface becomes visible and a tendency to tooth sensitivity, recolouration of the root surface and even tooth decay may appear. This exposed part of the root of the tooth is covered in dentine and is yellowish as opposed to the enamel covering the crown part of the tooth.
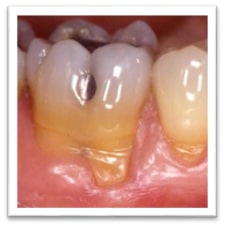
Knowing the reasons makes it easy to avoid them, prevent them early and postpone aggressive gum tissue loss in the future. Some risk factors can call for aggressive and fast-moving gum retreat, while under the influence of others it progresses less rapidly and distinctly, hence slower. Some of the most affecting:
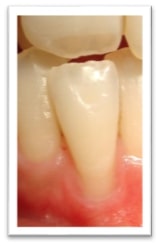
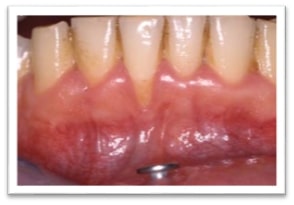
The most common symptom is the retreat of gum tissue along the root surface, exposing the yellowish dentine. Depending on the risk factors that call for gum retreat, one localised tooth, some teeth or even all on the same surface, several or even all around the crown section of the tooth, can be affected.
Most common symptoms: sensitivity, yellow root surfaces, dyed teeth, susceptibility to tooth decay, long teeth, gaps between teeth, penetration of food.
Several approaches and treatments depend on reason as well as breadth.
Periodontal treatment – will prevent further periodontal tissue loss and risk of progression of gum retreat.
Smoking cessation – in gum tissue, blood supply and microcirculation will slowly but significantly recover.
Brushing your teeth with a soft toothbrush – using a soft toothbrush, brushing your teeth for proper movements 2 times a day will significantly reduce the risk of further gum retreat.
Surgical options for gum retreat correction – if the patient is visually unsatisfied with the reasons for gum retreat, as well as complaints such as tooth sensitivity, which can be reduced using both toothpaste and rinses, then surgical options may be considered. Most commonly, gum tissue is transferred by surgery covering exposed root surfaces and, depending on the clinical situation, by additional use or non-use of soft tissue graft. For the most part, graft is taken from the patient’s own palate, but industrially processed graft can also be used.
To undergo this type of surgery, the patient’s gum tissue must be healthy, showing no signs of inflammation and, of course, only after a prior thorough examination.
In order to see if it is possible to close exposed root surfaces in your case and obtain additional information, it is recommended to apply for consultations with our clinic specialists Dr. Grīnvaldes, Dr. Lauriņas.